Preparing for the global transformation
driven by climate change
and from the scientific and technological revolution
We can do this with justice, or without justice.
The choice is ours.
26 June 2019:
Global Day of Workplace Action:
The discussion begins in every workplace
to Climate Proof Our Work
proclaimed by
International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC)
(207 million member workers in 163 countries and 331 affiliated national trade unions).
See the Guide to participate in the World Day
.
 See
See
 See
See
See the Guide to the right transition
A basket of disruptive technologies and work structures that are rapidly transforming the world of work.
If we can guide the implementation of these new technologies, we can create quality work with reduced working time and improved occupational health and safety.
The day of overcoming the possibilities of the Earth
(Earth Overshoot Day)
in 2019 it is calculated on 29 July

This is the day when humanity ended the budget of nature for the whole year
Earth Overshoot Day
:Every year we anticipate and in 2019, Earth Overshoot Day is the most anticipated ever.
This means that humanity now uses natural resources 1.75 times faster than the planet's ecosystems can regenerate. In other words, humanity uses 1.75.
The good news is that if we move the Earth Overshoot Day five days a year, we will use less than 1 Earth before 2050. The solutions are readily available. Opportunities for action include initiating a population dialogue, launching workplace programs, reducing food waste and petitioning governments to manage natural resources responsibly.
We can reverse the trend. We believe it is possible. Together, let's grow the movement
European Academies' Science Advisory Council
The new Easac report highlights an "alarming range of health risks due to climate change and the benefits of rapidly eliminating fossil fuels".
A collection of independent scientific studies that confirm the effects of climate change on human health.
The Council of European Science Academies (Easac), which brings together scientists from 27 European academies, calls for urgent political decisions to protect the health of the population in Europe.
See: Decarbonisation of Transport: options and challenges
See: The imperative of climate action to protect human health in Europe
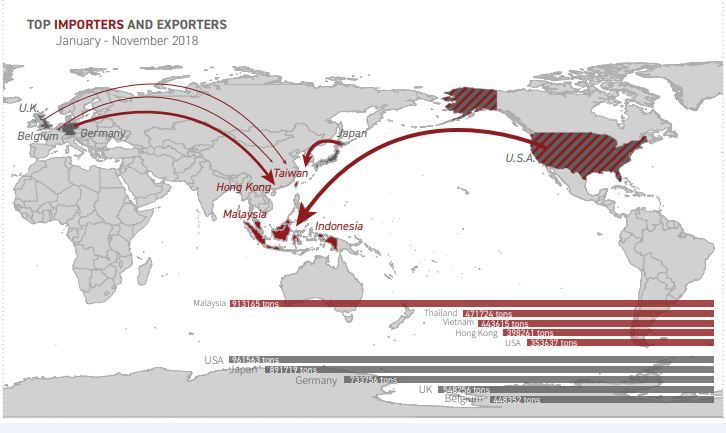
The 14th Meeting of the Conference of Parties to the Basel Convention today agreed to include mixed, unrecyclable and contaminated plastic waste exports into the control regime that requires the consent of importing countries before waste exports can proceed. The decision was hailed by the vast majority of the 187 nations present as well as by the Convention's environmental watchdog organization -- Basel Action Network (BAN) along with other civil society groups in attendance, as a breakthrough for environmental justice and an ethical circular economy.
ILO: Work-related fatalities reach 2 million annually
Two million workers die each year through work-related accidents and diseases and that is just the tip of the iceberg, the International Labour Organization (ILO) reported today.
Latest ILO estimates for the year 2000 show that annually there are two million work-related deaths - more than 5,000 every day - and for every fatal accident there are another 500-2,000 injuries, depending on the type of job. In addition, the ILO said for every fatal work-related disease there are about 100 other illnesses causing absence from work.
According to the ILO figures, the biggest killer in the workplace is cancer, causing roughly 640,000 or 32 per cent of deaths, followed by circulatory diseases at 23 per cent, then accidents at 19 per cent and communicable diseases at 17 per cent. Asbestos alone, the report says, takes some 100,000 lives annually.
Worse still, 12,000 children die each year working in hazardous conditions.
Agriculture, in which more than half of the workers of the world are employed, claims more than 50 per cent of occupational fatalities, injuries and diseases.
AGENDA 2030: Helping governments and stakeholders make the SDGs a reality
The technologies themselves are not the problem; it is the logic driving their introduction, which at this time is to reduce labour costs and labour standards.
A transition will take place.
We can do
• a violent scramble for desperate last-minute survival measures that completely dismiss human rights and social protection
• or an orderly and Just Transition that respects and protects present-day workers while creating new decent work in sustainable industries
The transition to a cleaner, more sustainable economy must be economically and socially just and fair for workers and their communities.
In particular with large multinational corporations the principles of sustainable industrial policies and a Just Transition should be baked into collective agreements.
• It is the subject of the Solidarity and Just Transition Silesia Declaration adopted at COP24 in 2018.
• t is defined in ILO’s Guidelines for a Just Transition towards Environmentally Sustainable Economies and Societies for All.
• Investment in Just Transition programmes is explained by the organization Principles for Responsible Investment in their document Climate change and the Just Transition: a guide for investor action.
• It is reflected in the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
Climate change is a serious threat to the well-being of everyone and its main cause is human activity. The evidence is irrefutable.
Scientists of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change have issued a stern warning: the world has approximately a 12-year window in which to act if we are to keep global average warming to less than 1.5 C above pre-industrial levels and avoid environmental catastrophe.

Sustainable industrial policies and plans
Sustainable industrial policies treat the environment, the economy, and society in an integrated manner.
• They must be based on a commitment to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
• Sustainable industrial policies must ensure that favoured industries create safe and healthy workplaces with workers’ rights to know about the hazards of work, to refuse/shut down unsafe work, and to fully participate in health and safety policies, programmes and procedures..
• Each community should have a specific action plan, including plans for investing in and developing low-carbon industries, renewable energy production and storage, and improved energy efficiency.
Creating decent work must be a goal of sustainable industrial policies.
China’s energy plans
China is leading the pack with more renewable energy capacity installed (around 550 GW in 2016) than any other country, with some major projects, and more investment than anyone else. It is also shutting coal plants, in part as a response to the massive air quality problems that emerged after its breakneck economic expansion based mainly on coal.
The nation is also experimenting with a carbon market. Clearly it wants to get on top of the carbon problem, although that may mean it just imports more gas, which also offers a partial and short-term response to the air pollution issues.
Info
What is the circular economy about?
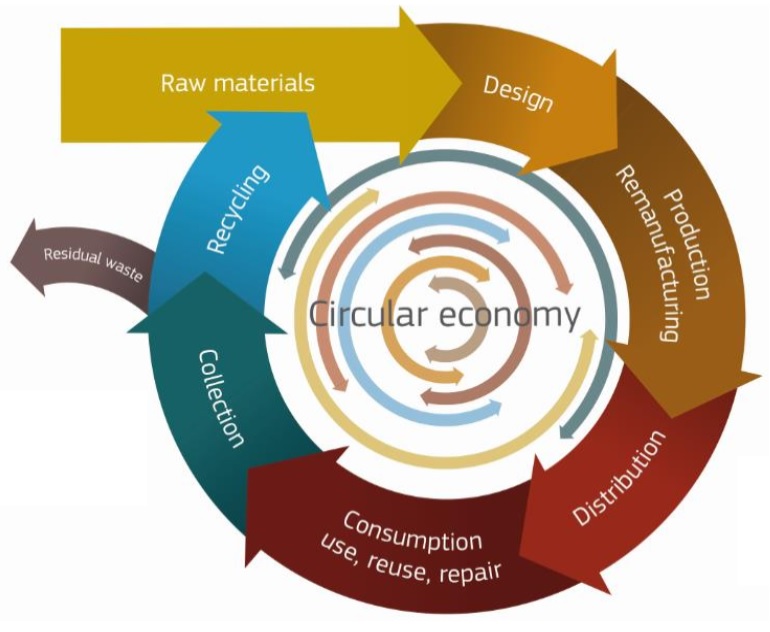
A circular economy aims to maintain the value of products, materials and resources for as long as possible by returning them into the product cycle at the end of their use, while minimising the generation of waste. The fewer products we discard, the less materials we extract, the better for our environment.
This process starts at the very beginning of a product’s lifecycle: smart product design and production processes can help save resources, avoid inefficient waste management and create new business opportunities.
This makes it possible to extend the life time of the products (today forced into the logic of programmed obsolescence), increasing the maintenance and adjustment services of the functions, also rationalizing the standards of the components.
What are the benefits?
The circular economy offers an opportunity to reinvent our economy, making it more sustainable and competitive. This brings benefits for European businesses, industries, and citizens such as:
• the development of new materials capable of being regenerated and of biomaterials;
• more innovative and efficient ways of producing and consuming;
• protection for businesses against scarcity of resources and volatile prices;
• opportunities for local jobs and social integration;
• optimisation of waste management which boosts recycling and reduces landfill;
• energy savings as less production processes requires less energy;
• renewable energy production;
• away of fossil fuels both for energy production and transport;
• better redistribution of production activities and maintenance and assistance services and therefore of workplaces, promoting reparability, feasibility, sustainability and recyclability of products;
• benefits for the environment in terms of climate and biodiversity, air, soil and water pollution.
 Leggi
Leggi
The success of the circular economy is permitted from the scientific and technological revolution (that include advanced digitalization, artificial intelligence, semi-autonomous interconnected machines, advanced robotics, 3-D printing, nanotechnology, advanced biotechnology, and platform work, among others.).
Products and services designed in a circular way can minimise resource use and foster materials’ reuse, recovery and recyclability down the road. Ecodesign and Energy Labelling measures for several products now include rules on material efficiency requirements such as availability of spare parts, easeof repair, and facilitating end-of-life treatment.
The action plan promoted for the first time a systemic approach across entire value chains. With it, the Commission has mainstreamed circular principles into plastic production and consumption, water management, food systems and the management of specific waste streams. This was made possible by strong support and engagement of Member States, the 2European Parliament, the business community and citizens. It has also contributed to moving towards the achievement of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
Stakeholder engagement is vital for the transition. The systemic approach of the action plan has given public authorities, economic actors and civil society a framework to replicate in order to foster partnerships across sectors and along value chains.
• 2019: by 2030 to change development and to avoid disaster
• TOGETHER WE CHOOSE HOW TO CHANGE DEVELOPMENT
• THERE IS A LITTLE TIME TO CHANGE THE DEVELOPMENT
• we must choose together
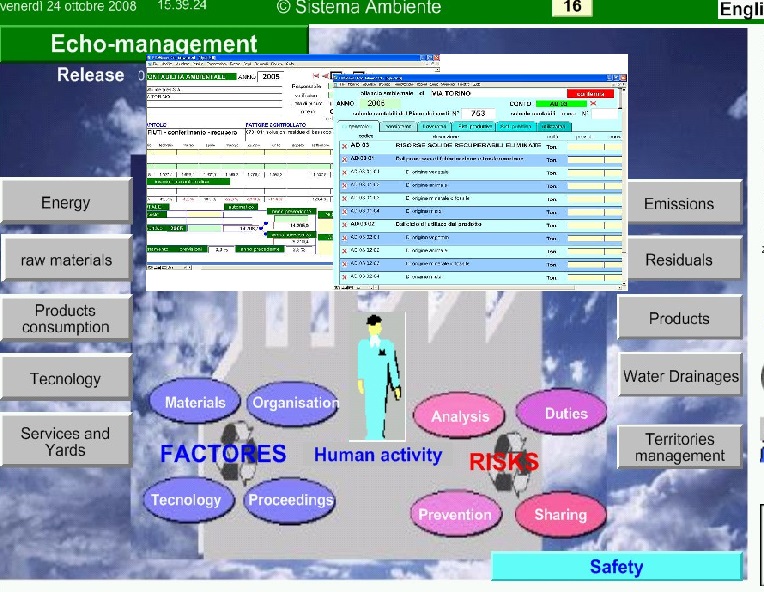
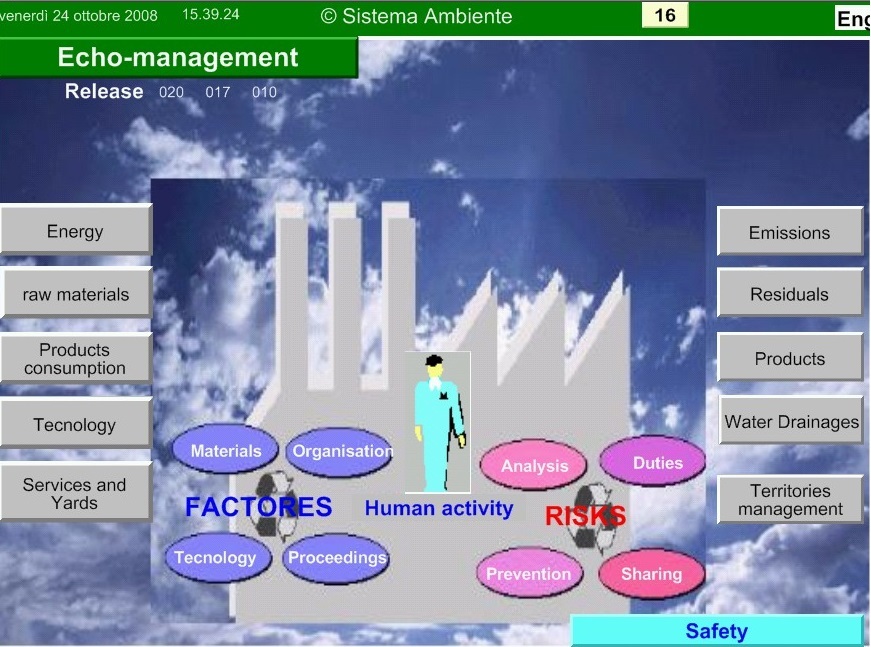
"SISTEMA AMBIENTE" IS THE INFORMATION AND MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
TO CROSS THE CHANGE
http://www.sistemaambiente.net/Tesi/Implementation_of_a_QHSE_management_system_FENG_Meng_Ting.pdf
To go on from the squandering management (with its high costs both for the company and for the system) to a circular economy, a functional tool is needed that, in the model of "Sistema Ambiente", it is the environmental balance fed by the environmental accounting (the relative quantitative values the progress and the destination of the resources along the cycle of the material and the impact that they have in the system in which the company is inserted) and the industrial accounting. The making at company level allows to begin the balances of area and sector with a compound method.
“Sistema
Ambiente”,the system of management of Digitalis, in addition to the utility of normal record and production of documents of treatment of residues, offers some important opportunities for a better waste processing organization.
First of all, the possibility of linking the residue and its handling to the individual process phases: this allows to obtain quantitative and qualitative information that are more efficacies, useful to produce a reduction and a qualification of the wastes.
Secondly, with the tool of environmental accounting and of the environmental balance of the product, it is possible to have a more effective impact to know: what to change into the materials, into the process and into the design and the composition of the product
http://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2017/581913/EPRS_STU%282017%29581913_EN.pdf
The Environmental Balance also includes the calculation of the equivalent carbon: calculation that is prepared in every aspect of the cycle of production (the energy consumption in processes and products, the way of transport of the workpeople and the used one for materials and products, manufacture of the raw material, the residues produced by the processes and the end of the useful life of the products). The calculation is the base to understand how to modify the processes and to plan how to reduce the gas emission of greenhouse effect produced by the cycle.
http://www.bilans-ges.ademe.fr/en/accueil/contenu/index/page/principles/siGras/0